Cryptocurrency Taxes in India 2024 : A Comprehensive Guide
Cryptocurrencies, heralded as the forefront of technological evolution in finance, are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security.
Unlike traditional currencies, they are decentralized and typically operate on a technology called blockchain which allows every transaction to be public and secure, but anonymous at the same time. Popular examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple.
These currencies can be used for a variety of financial transactions, purchasing goods and services, and as investments.
Cryptocurrency Regulation in India: A Historical Overview
The journey towards the regulation of cryptocurrencies in India has seen numerous twists and turns. Starting in 2013, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) warned users, holders, and traders about the potential financial, operational, legal, and security-related risks associated with dealing in such virtual currencies.
1. 2013 Advisory and the Ensuing Uncertainty
The initial warnings by the RBI in 2013 did little to dampen the enthusiasm for these digital assets, although they cast a shadow of uncertainty over their use. This advisory was aimed more at cautioning the populace rather than enforcing any actual regulatory measures.
2. 2018 RBI Ban
By April 2018, as the volume and value of cryptocurrencies soared globally, the RBI issued a more stringent directive, effectively banning banks and other regulated financial institutions from providing services to any individual or business dealing in virtual currencies. This led to a significant outage of legal banking support for the crypto exchanges and other related businesses.
3. 2020 Supreme Court Ruling
The 2018 ban saw numerous appeals and court cases filed by various stakeholders within the Indian crypto community. It culminated in a landmark judgment by the Supreme Court in March 2020, where the ban was overturned.
The court ruled that the RBI’s action was disproportionate to the risks that were presented by the digital currencies. This decision injected a new lease of life into the cryptocurreny market in India.
4. Budget 2022 and Crypto Taxation
Recognizing the growing relevance of cryptocurrencies, the Indian government formally addressed their taxation in the Union Budget 2022 presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
As detailed in the 2022 Budget, the government categorized cryptocurrencies and NFTs as “Virtual Digital Assets” (VDAs) and introduced specific tax provisions – highlighting a significant step towards incorporating these digital assets into the formal economic framework of the country.
Implications of Cryptocurrency Regulation
The formal classification of cryptocurrencies as Virtual Digital Assets in 2022 has led to increased interest from both individual investors and businesses looking to explore this burgeoning field.
However, with this comes the responsibility of fulfilling one’s tax obligations, outlined under the new regulations which can be examined under the income tax services provided by tax experts.
Engaging with professionals can provide in-depth understanding and compliance assistance, right from filing income tax returns to complex income tax litigation.
These developments signal a gradually maturing approach towards cryptocurrencies in India—one that recognizes both their potential risks and benefits.
For investors and users, staying informed about the legislative landscape is crucial. Not only does this ensure compliance, but it also helps in making informed decisions which is pivotal given the volatile nature of digital assets.
For a detailed look into the benefits of timely and compliant tax filings, this guide on the benefits of filing income tax returns might be a great starting point.
This brings us to the need for understanding the specific tax obligations that come with trading or investing in cryptocurrencies.
Crypto Taxation Laws in India
Overview of Tax Implications for Cryptocurrencies
As detailed in the Union Budget 2022 and various subsequent announcements, the Indian government has implemented specific tax measures to regulate the burgeoning field of cryptocurrencies.
Here’s what every crypto investor and trader needs to know:
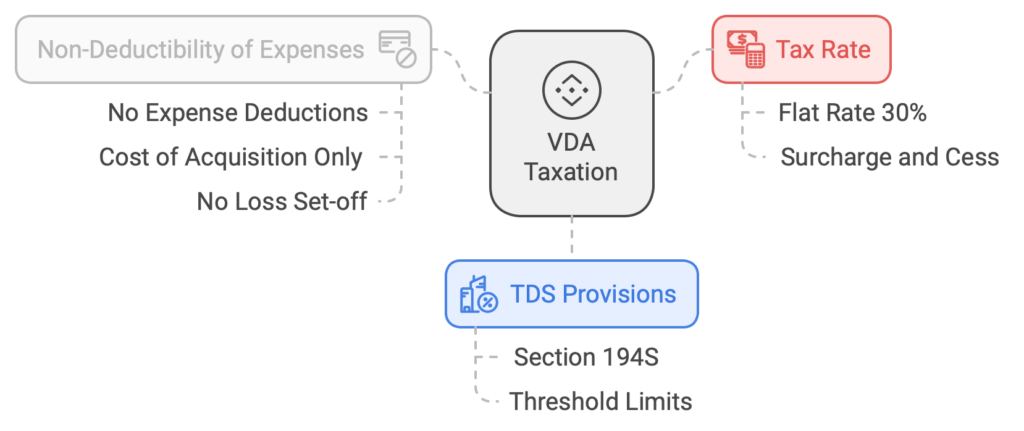
1. Taxation of Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs)
Cryptocurrencies and NFTs have been officially classified under a new category called Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs).
The tax regulations around these assets are covered under Section 115BBH, which was introduced in the Union Budget 2022.
- Tax Rate: The income from the transfer of cryptocurrencies and other virtual digital assets is taxed at a flat rate of 30%, plus applicable surcharge and health & education cess.
- TDS Provisions: Section 194S mandates a 1% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on the transfer of such assets over certain thresholds.
2. Non-Deductibility of Expenses
A unique aspect of VDA taxation is that no deduction for any expense or allowance is allowed against the income from transfer of VDAs, except for the cost of acquisition. This strict provision ensures that the calculation remains straightforward but can significantly impact the net gains from such transactions.
3. No Set-off of Losses
Investors cannot offset losses from the transfer of one VDA against the income from another VDA or any other source of income. This restriction was particularly important to maintain the distinctive tax treatment of these digital assets.
Detailed Tax Processes for Cryptocurrency Transactions
Calculating Tax on Crypto
To calculate your tax liability from cryptocurrency transactions, you’ll need to consider the following:
- Sale Price: The final amount at which you sell your cryptocurrency.
- Cost Base: The original cost of acquiring the cryptocurrency.
- Taxable Gain: Sale Price minus Cost Base.
Here’s a simple formula you can use:
[ {Taxable Gain} = {Sale Price} – {Cost Base} ]
[ {Tax Due} = {Taxable Gain} \times 30\% \plus \{applicable cesses and surcharges} ]
Crypto Bookkeeping:
Given the complexity and the volume of transactions that can occur with cryptocurrencies, maintaining accurate records is crucial.
To aid in this, numerous software tools are available that can help consolidate transactions from various exchanges and wallets, classify them appropriately, and prepare detailed capital gains reports and other necessary documentation for tax purposes.
Reporting Crypto Transactions in Income Tax Returns
Starting from the financial year 2022-23, all taxpayers who have conducted transactions in cryptocurrencies must report these under the newly introduced ‘Schedule VDA’ in their Income Tax Returns.
Whether you are filing as an individual or on behalf of a business entity, accurate and timely reporting of all transactions involving VDAs is crucial to remain compliant with the Indian tax laws.
Investors and traders need to ensure that they account for the TDS deducted at source and claim credit for the same against their total tax liability. Here is where detailed bookkeeping and diligent compliance practices play a vital role.
Use of Tax Advisory Services
Navigating the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation can be challenging. It is advisable to engage with qualified tax professionals who can offer comprehensive tax advisory services.
This ensures compliance with tax laws and can help in strategically planning transactions to optimize tax obligations.
Part Three: Advanced Tax Scenarios and Strategic Tax Planning for Cryptocurrency
Handling Different Types of Crypto Income
Cryptocurrency earnings can stem from various activities, each with its own tax implications:
- Mining: Income from mining is taxed as business income at the flat rate of 30%. The cost of acquisition is considered zero, and expenses like electricity or infrastructure cannot be deducted.
- Staking/Forging: The rewards from staking or forging are considered income from other sources and taxed at 30%. When these assets are sold, any gains are also subject to the same tax rate.
- Airdrops: Income from airdrops is taxed the moment it is received, based on the fair market value, and any subsequent gains at the point of sale are also taxed at 30%.
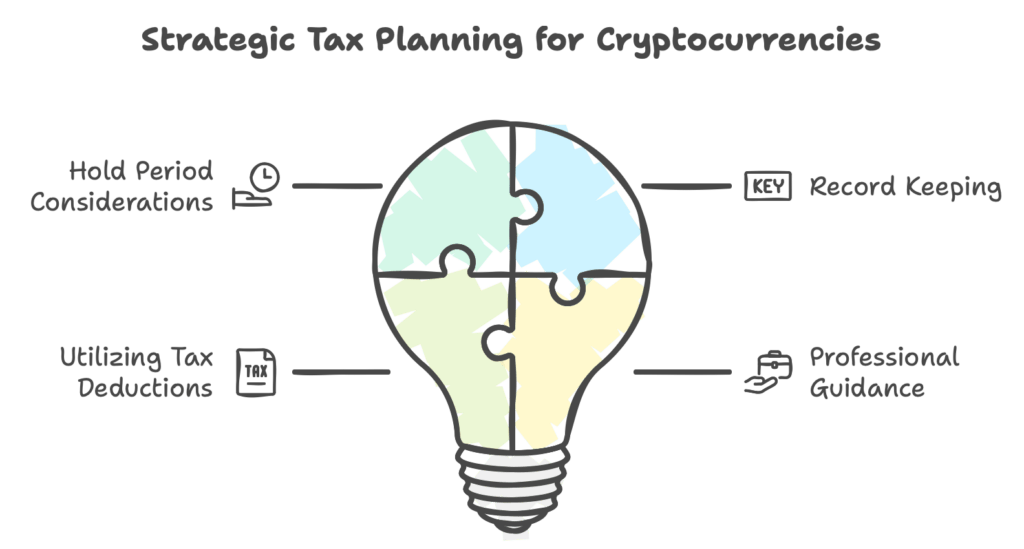
Tax Planning Strategies for Crypto Investments
Given the rigid structure of tax laws surrounding cryptocurrencies, smart planning is essential:
- Hold Period Considerations: Since both short-term and long-term capital gains are taxed at the same rate, the decision to sell should be based more on market conditions than tax considerations.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all transactions to support claims and deductions, such as the cost of acquisition.
- Utilizing Tax Deductions: While few deductions are allowed, ensuring that all permissible deductions (like the cost of acquisition) are claimed is crucial.
- Professional Guidance: Engage with financial advisors and tax professionals to help navigate complex transactions and reporting requirements.
Compliance and Disclosure Requirements
It’s vital for both individuals and businesses involved in cryptocurrencies to comply with the regulatory requirements:
- Companies: As mandated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), Indian companies must disclose cryptocurrency holdings and transactions in their financial statements, which helps in corporate governance and provides clarity to stakeholders.
- Individuals: Individual investors should also be diligent in disclosing their transactions in cryptocurrencies, especially in their tax returns under the ‘Schedule VDA’.
Utilizing Technology for Compliance
The use of advanced software and tools can significantly help in managing the complex nature of cryptocurrency transactions:
- Tax Software: Utilizing dedicated crypto tax software can help consolidate transactions from various platforms, automatically calculate gains or losses, and assist in accurate tax reporting.
- Integration of APIs: To manage real-time data from multiple cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets, APIs can be integrated into personal finance management tools, aiding in seamless bookkeeping.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Navigating the tax implications of cryptocurrencies requires a combination of diligent record-keeping, up-to-date knowledge of tax laws, and strategic planning.
The evolving nature of this space means regulations can change, and staying informed is paramount. Especially as cryptocurrencies become more integrated into mainstream finance, the potential adjustments in their regulation and taxation will necessitate continuous learning and adaptation.
Engaging with professionals through services like Ahuja & Ahuja’s tax planning and litigation services not only ensures compliance but also helps in leveraging cryptocurrencies as part of a balanced financial portfolio effectively.
Disclaimer
The materials provided herein are solely for educational and informational purposes. No attorney/professional-client relationship is created when you access or use the site or the materials. The information presented on this site does not constitute legal or professional advice and should not be relied upon for such purposes or used as a substitute for professional or legal advice.




